Dupilumab is an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor monoclonal antibody approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) with remarkable safety and efficacy profiles. However, former studies have reported an increase in serum eosinophils during treatment, with undetermined clinical significance.
The objective of this study is to evaluate changes in blood eosinophils and other laboratory parameters while on dupilumab.
MethodsWe conducted a multicenter, prospective, observational study from 2018 to 2022 with adolescent and adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab from Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves, Spain, and Coimbra University Hospital, Portugal. Clinical scoring of the dermatitis, complete blood count, total serum IgE and LDH levels were collected at baseline and on weeks 8, 16, 24 and 48.
ResultsWe included a total of 81 patients (41 women/40 men; mean age of 30.86±12.26 years). Clinical and demographic characteristics were similar across centres. AD severity scales (EASI, SCORAD, ItchVAS and SleepVAS) showed sustained improvement from week 8 of treatment onwards. Eosinophil levels were significantly higher on week 16 (0.69×103/μL) vs baseline (0.41×103/μL) (p=0.018) and returned to baseline levels on week 48 (0.59×103/μL, p>0.05). LDH and IgE levels decreased during the study.
ConclusionOur study showed a significant clinical improvement of AD but a mild and self-limited increase in eosinophil levels on week 16, not associated with any clinical signs. Therefore, elevated serum eosinophil levels in AD patients on dupilumab does not seem clinically relevant and should not condition treatment withdrawal.
Dupilumab es un anticuerpo monoclonal inhibidor de la IL-4/IL-13 aprobado para el tratamiento de la dermatitis atópica (DA) con perfiles de eficacia y seguridad notables. Sin embargo, estudios previos han informado de un aumento de los eosinófilos séricos durante el tratamiento, con un significado clínico indeterminado.
El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar los cambios en los eosinófilos en sangre y otros parámetros de laboratorio durante el tratamiento con dupilumab.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio observacional prospectivo multicéntrico entre 2018 y 2022 con pacientes adolescentes y adultos con DA moderada a grave tratados con dupilumab del Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves, España, y del Hospital Universitario de Coimbra, Portugal. Se recogieron puntuaciones clínicas de la dermatitis, hemograma completo, IgE sérica total y niveles de LDH al inicio y en las semanas 8, 16, 24 y 48 de tratamiento.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 81 pacientes (41 mujeres/40 hombres; edad media de 30,86±12,26 años). Las características clínicas y demográficas fueron similares entre centros. Las escalas de gravedad de la DA (EASI, SCORAD, ItchVAS y SleepVAS) mostraron una mejoría sostenida a partir de las 8 semanas de tratamiento. Los niveles de eosinófilos fueron significativamente mayores en la semana 16 (0,69 x103/μL) que al inicio (0,41 x103/μL) (p=0,018) y volvieron a los niveles basales en la semana 48 (0,59 x103/μL, p>0,05). Los niveles de LDH e IgE disminuyeron durante el estudio.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio mostró una mejoría clínica significativa de la DA de los pacientes tratados con dupiluman, con un aumento leve y autolimitado de los niveles de eosinófilos en la semana 16, no asociado a ninguna manifestación clínica. Por lo tanto, el aumento de los eosinófilos séricos en pacientes con DA tratados con dupilumab no es clínicamente relevante y no debe condicionar la suspensión del tratamiento.
Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4R-α and IL-13R-α1 inhibiting IL-4 and IL-13 signalling, which are pivotal for the inflammatory cascade and compromised skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis (AD).1 Dupilumab acts specifically to downregulate the downstream signalling events that cause the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and the recruitment of immune cells responsible for the clinical signs of AD.1
Dupilumab became the first biologic agent approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD, with high efficacy and a good safety profile vs former therapeutic options, such as cyclosporine, azathioprine, methotrexate or mycophenolate mofetil.2,3 Reported adverse effects include transient local erythema and oedema at the injection site, ocular surface disease, eczematous paradoxical reactions in the head and neck, psoriasis-like eruptions, arthralgia and arthritis and alopecia, with systemic adverse effects being extremely rare.2
Elevated blood eosinophil levels while on dupilumab were already noted in clinical trials. However, as there is no formal recommendation to control analytical values while on dupilumab it remains unclear how frequently dupilumab-related eosinophil elevation occurs in real world conditions. In fact, a recent retrospective study reported no significant serum eosinophil elevation, even a normalization of these values while on dupilumab.4
The primary endpoint of this study is to evaluate blood eosinophil levels in adolescent and adult AD patients while on dupilumab to define the timing, size, and clinical implications of high eosinophil levels. Secondary endpoints intended to correlate eosinophil levels with other analytical parameters, such as serum IgE and Lactate dehydrogenase.
MethodsStudy design and participantsA multicentre ambispective (retrospective and prospective) observational study was conducted from April 2018 to June 2022, in the Department of Dermatology of Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves, Granada, Spain and the Department of Dermatology, Coimbra University Hospital, Portugal.
Eligible participants were adolescents (>12 years old) and adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD scheduled to start treatment with dupilumab for the first time and who signed an informed consent form after being explained the objectives of the study.
Exclusion criteria were cutaneous or systemic infection—namely HIV infection—history of cancer, immunological disease, and use of systemic antibiotics.
In adult patients, dupilumab 300mg was administered subcutaneously every 2 weeks after a loading dose of 600mg, whereas adolescents (12–17 years old) received a loading dose of 400mg followed by a 200mg dose every 2 weeks or the adult posology if they weighed>60kg.
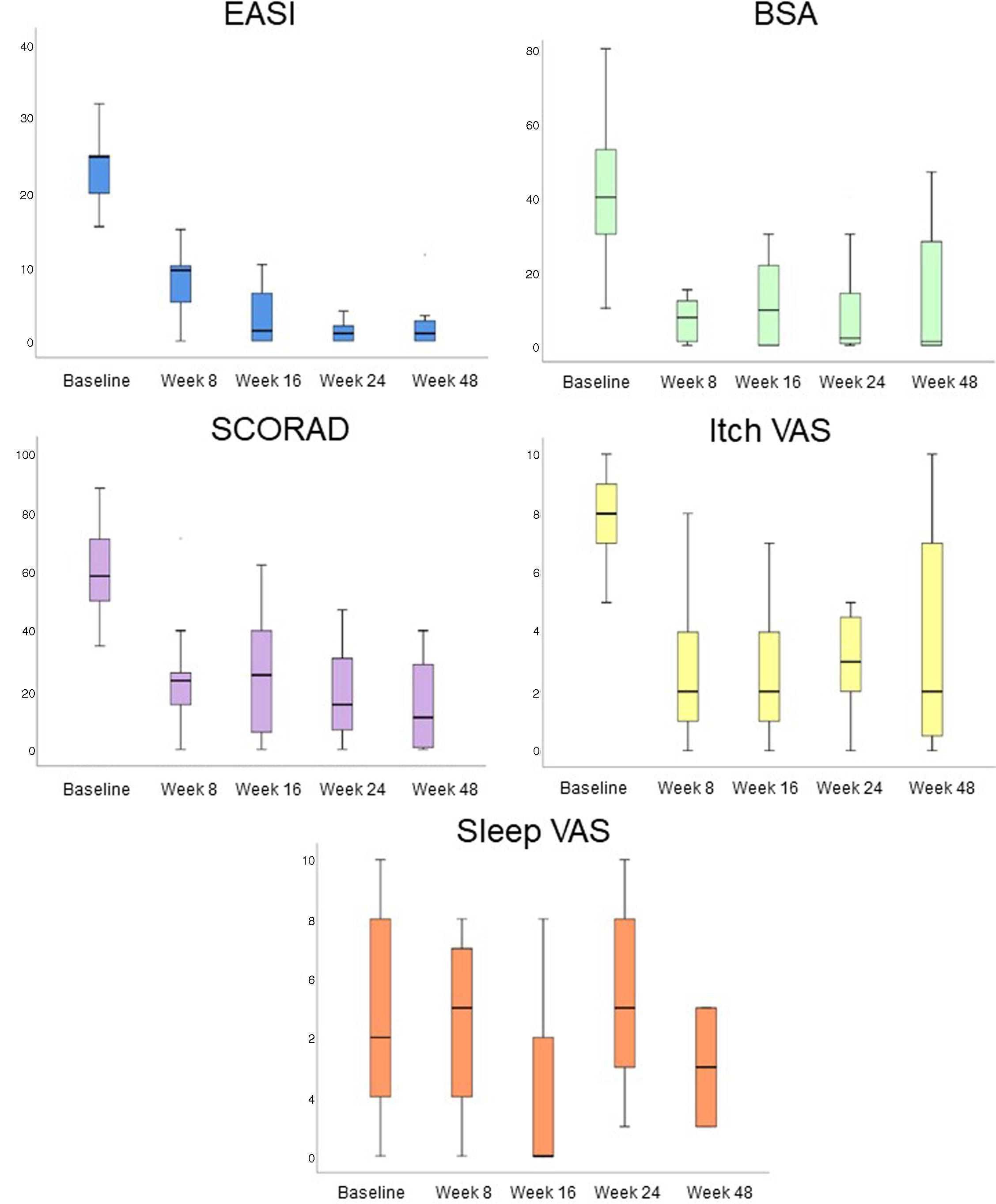
Outcomes and measuresWe collected data on age, sex, age of disease onset, family history of AD, history of asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis and food allergies, previous treatments and assessed AD severity at baseline and on weeks 8, 16, 24 and 48 using the EASI (Eczema Area Severity Index), SCORAD (SCORing Atopic Dermatitis), BSA (Body Surface Area), Itch Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Sleep VAS scores. At the same time points, fasting venous blood was collected and the following parameters were evaluated: leucocyte count, neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes and basophils, total serum IgE and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
Statistical analysisDescriptive statistics were used to present sample characteristics. Continuous data were expressed as mean (standard deviation) and qualitative data as relative (absolute) frequency. The Shapiro–Wilk test and the Skewness/Kurtosis were used to determine the normality of data distribution and Levene's test was employed to check the homogeneity of variance, Student's t-test for independent samples was used to compare quantitative variables across different populations, and the Student's t-test for paired samples was used to compare differences in parameters across different weeks of treatment. Statistical significance was defined as a two-tailed p<0.05. SPSS version 25.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analyses.
EthicsThis study was approved by Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves ethics committee (Analytical biomarkers in patients with atopic dermatitis).
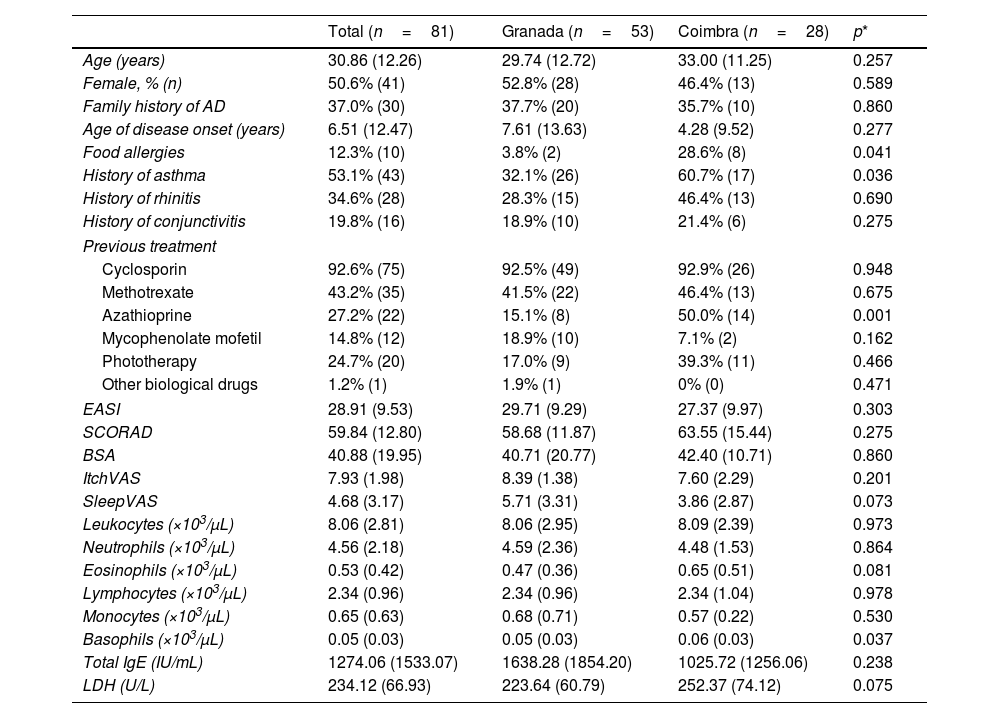
ResultsBaseline demographics and clinical characteristicsA total of 81 patients (41 women/40 men); mean age, 30.86 (12.26) years with moderate-to-severe AD; and mean EASI, 28.91 (9.53) were included in the study, 53 (65.4%) from the Spanish hospital and 28 (34.6%) from the Portuguese one, with similar characteristics (Table 1). Disease onset occurred at 6.51 years, approximately 60% had a past medical history of allergic conjunctivitis, asthma, or allergic rhinitis; all patients had been administered previous systemic treatments, most commonly cyclosporin (92.6%), (Table 1).
Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics at baseline.
| Total (n=81) | Granada (n=53) | Coimbra (n=28) | p* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 30.86 (12.26) | 29.74 (12.72) | 33.00 (11.25) | 0.257 |
| Female, % (n) | 50.6% (41) | 52.8% (28) | 46.4% (13) | 0.589 |
| Family history of AD | 37.0% (30) | 37.7% (20) | 35.7% (10) | 0.860 |
| Age of disease onset (years) | 6.51 (12.47) | 7.61 (13.63) | 4.28 (9.52) | 0.277 |
| Food allergies | 12.3% (10) | 3.8% (2) | 28.6% (8) | 0.041 |
| History of asthma | 53.1% (43) | 32.1% (26) | 60.7% (17) | 0.036 |
| History of rhinitis | 34.6% (28) | 28.3% (15) | 46.4% (13) | 0.690 |
| History of conjunctivitis | 19.8% (16) | 18.9% (10) | 21.4% (6) | 0.275 |
| Previous treatment | ||||
| Cyclosporin | 92.6% (75) | 92.5% (49) | 92.9% (26) | 0.948 |
| Methotrexate | 43.2% (35) | 41.5% (22) | 46.4% (13) | 0.675 |
| Azathioprine | 27.2% (22) | 15.1% (8) | 50.0% (14) | 0.001 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 14.8% (12) | 18.9% (10) | 7.1% (2) | 0.162 |
| Phototherapy | 24.7% (20) | 17.0% (9) | 39.3% (11) | 0.466 |
| Other biological drugs | 1.2% (1) | 1.9% (1) | 0% (0) | 0.471 |
| EASI | 28.91 (9.53) | 29.71 (9.29) | 27.37 (9.97) | 0.303 |
| SCORAD | 59.84 (12.80) | 58.68 (11.87) | 63.55 (15.44) | 0.275 |
| BSA | 40.88 (19.95) | 40.71 (20.77) | 42.40 (10.71) | 0.860 |
| ItchVAS | 7.93 (1.98) | 8.39 (1.38) | 7.60 (2.29) | 0.201 |
| SleepVAS | 4.68 (3.17) | 5.71 (3.31) | 3.86 (2.87) | 0.073 |
| Leukocytes (×103/μL) | 8.06 (2.81) | 8.06 (2.95) | 8.09 (2.39) | 0.973 |
| Neutrophils (×103/μL) | 4.56 (2.18) | 4.59 (2.36) | 4.48 (1.53) | 0.864 |
| Eosinophils (×103/μL) | 0.53 (0.42) | 0.47 (0.36) | 0.65 (0.51) | 0.081 |
| Lymphocytes (×103/μL) | 2.34 (0.96) | 2.34 (0.96) | 2.34 (1.04) | 0.978 |
| Monocytes (×103/μL) | 0.65 (0.63) | 0.68 (0.71) | 0.57 (0.22) | 0.530 |
| Basophils (×103/μL) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.06 (0.03) | 0.037 |
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | 1274.06 (1533.07) | 1638.28 (1854.20) | 1025.72 (1256.06) | 0.238 |
| LDH (U/L) | 234.12 (66.93) | 223.64 (60.79) | 252.37 (74.12) | 0.075 |
All AD severity scales significantly improved after dupilumab (Fig. 1). After 8 weeks on dupilumab, a decrease in the EASI (28.91 vs 7.45, p<0.001), SCORAD (61.50 vs 23.87, p<0.001), BSA (29.44 vs 6.62, p=0.002), Itch VAS (7.34 vs 3.09, p<0.001), and Sleep VAS (6.57 vs 5.43, p<0.001) scores was observed. This improvement was also significantly on week 48: EASI decreased a mean of 20.05 (9.20) points, p<0.001; SCORAD, 42.13 (36.5), p=0.37; BSA, 24.80 (22.53), p=0.043; and Itch VAS, 4.20 (2.77), p=0.028.
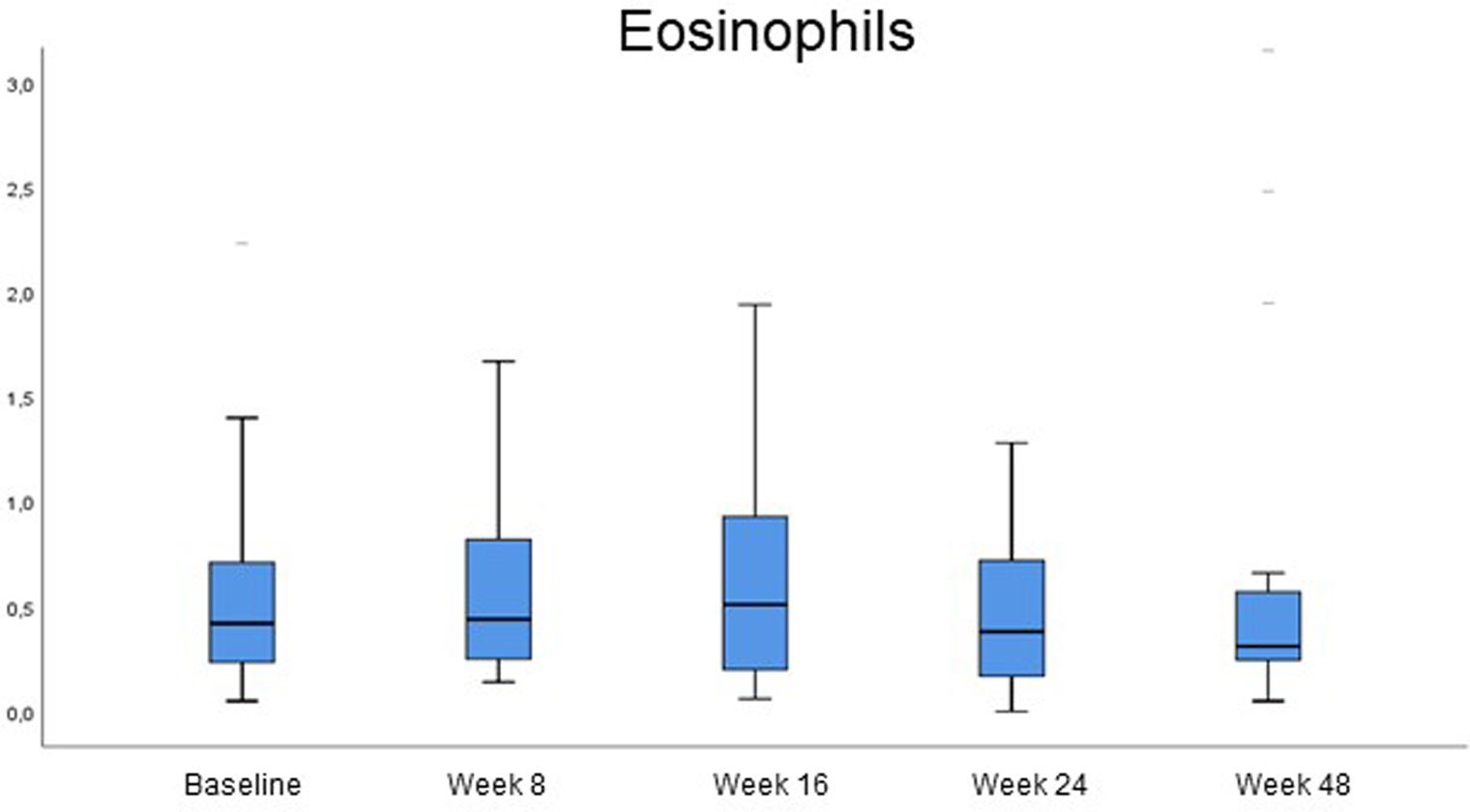
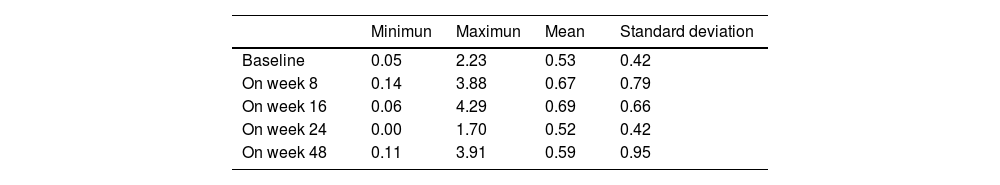
Analytical changes at the follow-upChanges in blood cell count were reported at the follow-up (Fig. 2, Table 2). The levels of eosinophils, which were already high at baseline (0.53×103/μL; SD, 0.42), did not change significantly within the first 8 weeks on dupilumab. However, a slight increase was reported between baseline and week 16 (0.53×103/μL vs 0.69×103/μL, p=0.018). On week 48, serum eosinophils returned to levels that were not significantly different vs baseline (0.59×103/μL, p>0.05).
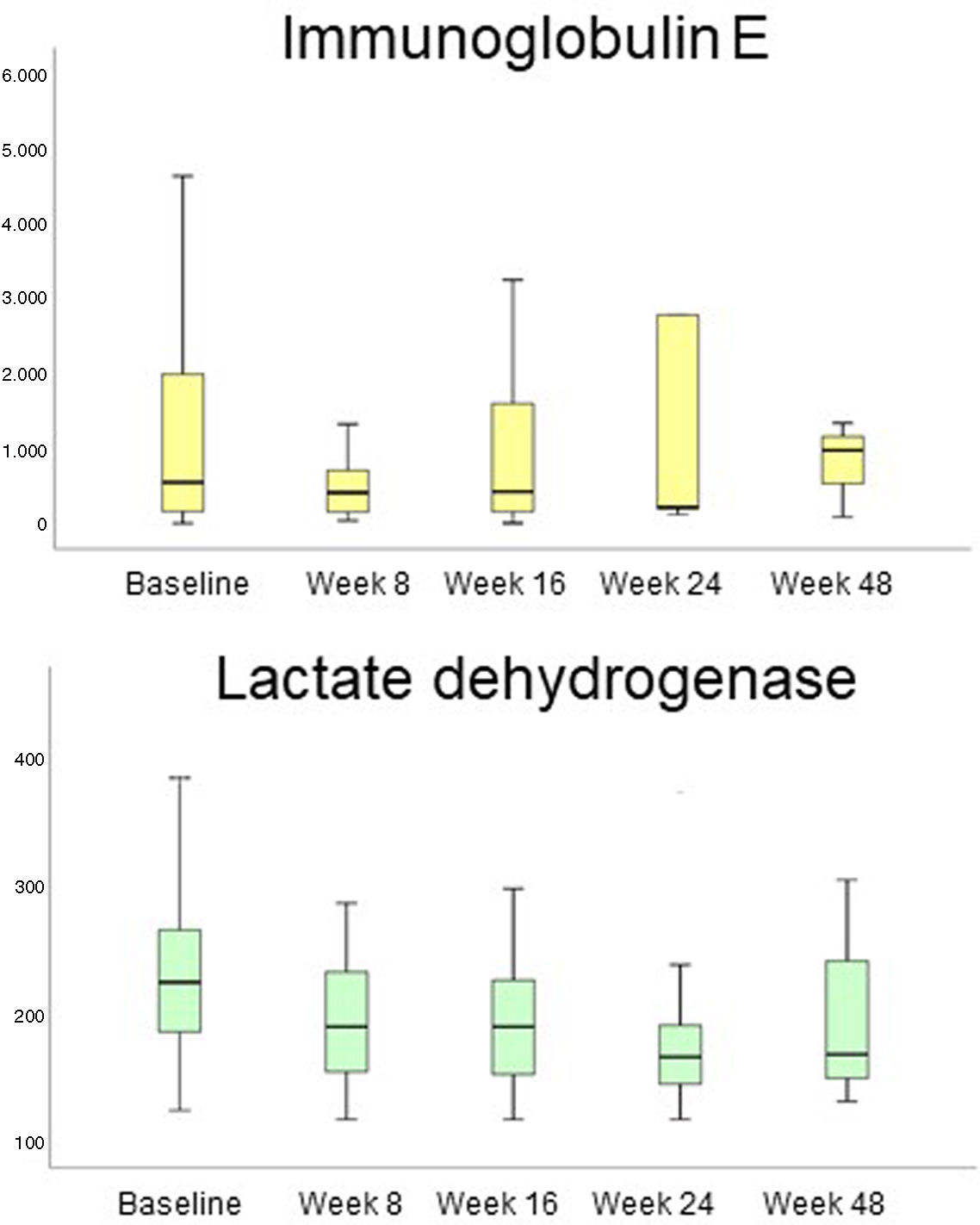
LDH and IgE decreased during the studied period (Fig. 3). LDH decreased comparing each study period: 234.12U/L (baseline) vs 192.04U/L (week 8), p=0.003; vs 195.07U/L (week 16), p=0.005; vs 181.29U/L (week 24), p=0.043; vs 191.94U/L (week 48), p=0.003). IgE decreased mainly from baseline to week 8 of treatment (1274.06IU/mL vs 647.80IU/mL; p=0.024). No other analytical changes were found.
Eosinophil levels increased most significantly in 9 patients (>1×103/μL), 7 of whom had atopic comorbidities. Two of these patients had asthma and rhinitis and already had high eosinophil counts at baseline (1.27 and 1.09×103/μL), along with a very high total serum Ig E (6193 and 42,298IU/mL). These 2 patients increased eosinophil count on week 8 up to 1.77 and 3.88×103/μL, respectively and the first patient even went up to 4.29×103/μL on week 16, always parallel to a sharp decrease in IgE down to 1681 and 15803IU/mL on week 16. Eosinophil values went back to normal after 1 year on therapy in all patients. No clinical signs or progression of atopic comorbidities or eosinophilia-related systemic signs were reported.
In the entire sample there was no statistically significant association between elevated eosinophil levels and IgE levels and any demographic or clinical parameter of these patients.
DiscussionThis study evaluated the clinical and analytical impact of dupilumab in a cohort of patients with severe AD and confirmed the expected clinical improvement.
The increase in circulating eosinophils associated with dupilumab therapy have previously been described as transient, mild, and unrelated to therapeutical success. Our results further confirm this trend. Although some patients can grow very high levels of circulating eosinophils, there was no associated progression of atopic or any other systemic signs and no patient had to discontinue therapy. The analysis did not yield any significant clinical impact in patients with dupilumab-induced eosinophil elevation and no correlation was ever found with IgE or LDH levels. Moreover, eosinophil levels went back to baseline values with continuation of therapy.
A similar elevation of blood eosinophils while on dupilumab had been noted in several studies. It has been reported that in AD and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, these changes are typically mild (with levels up to 3000cells/μL), transient, not associated with clinical symptoms or complications, and unrelated with a reduced efficacy of treatment.5 Moreover, as in previous research, patients with high levels of eosinophils at baseline are those who experience the greatest increases within the first few weeks on dupilumab. The exception is a case report of eosinophilic pneumonia in a 63-year-old patient with AD.6 Conversely, a subgroup of patients with severe asthma who started dupilumab developed eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis.7
The mechanism of eosinophil elevation while on dupilumab is still to be elucidated but was attributed to the inhibition of eotaxin-3, VCAM-1, and CCL17/TARC due to IL4/IL-13 blockade, which decreases eosinophil migration without an effect on eosinophilopoiesis.7 Other authors associated this increase with low number of CD203+basophils and higher CD23 expression in B cells in a subgroup of AD patients on dupilumab.8
Our analysis of results does clarify the pathological mechanism or the risk factors associated with this phenomena, and no statistically significant correlation between eosinophil elevation and demographic, clinical or analytical factors was ever found.
Regarding secondary endpoints, a transient IgE increase while on therapy has been reported in other studies.4 However, this was not the case in our patients, with IgE steadily decreasing while on dupilumab. Similarly, LDH also decreased progressively, reflecting a decrease in the inflammatory activity associated with clinical improvement as former studies have described.9
As far as we know, this multicenter study is the largest study on the impact of dupilumab on eosinophil count in a cohort of patients with severe AD. However, there are some limitations associated with it, namely those inherent to its retrospective and prospective design, such as the heterogeneity of the sample and the limited collection of analytical data.
ConclusionsWe conclude that although serum eosinophils do increase in a proportion of AD patients on dupilumab during the early months of therapy, this elevation is self-limited, mild, and not clinically relevant. Therefore, there is no need to discontinue dupilumab. Moreover, despite transient eosinophilia, based on the drug data sheet and the findings of this and other studies, routine laboratory follow-up is deemed unnecessary in patients on dupilumab.
FundingThis research was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III through the project PI23/01875. and TM-V was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (CM22/00083).
This study is a part of Carolina Montero-Vilchez's doctoral thesis at the Clinical Medicine and Public Health program of Universidad de Granada.