Chronic recurrent annular neutrophilic dermatosis (CRAND) is a descriptive term first used by Christensen et al.1 in 1989 to define a condition with findings suggestive of Sweet syndrome, but without accompanying fever or general symptoms. We present a rare case in which a patient with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) developed an extremely painful form of CRAND with a unique clinical course.
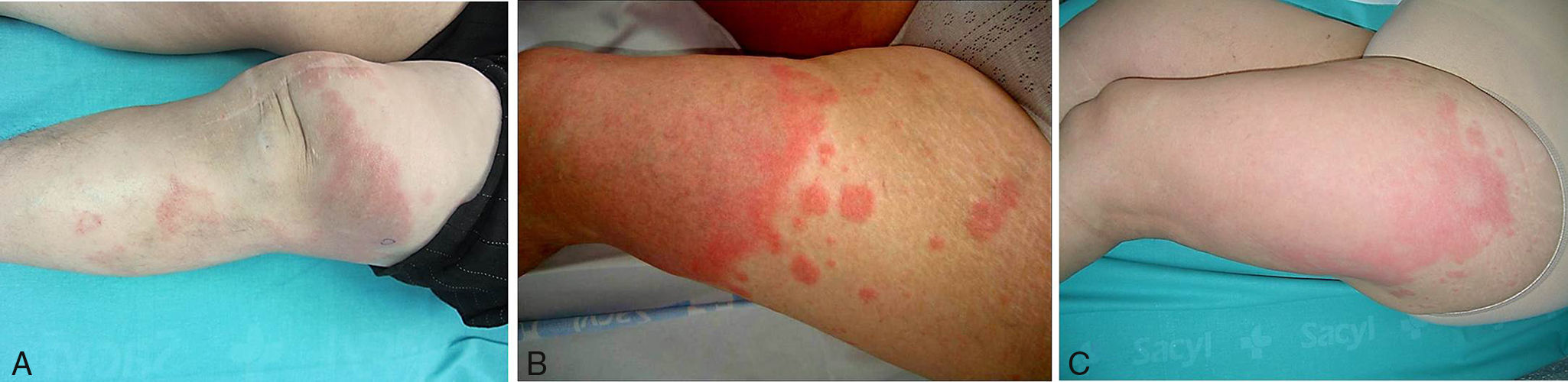
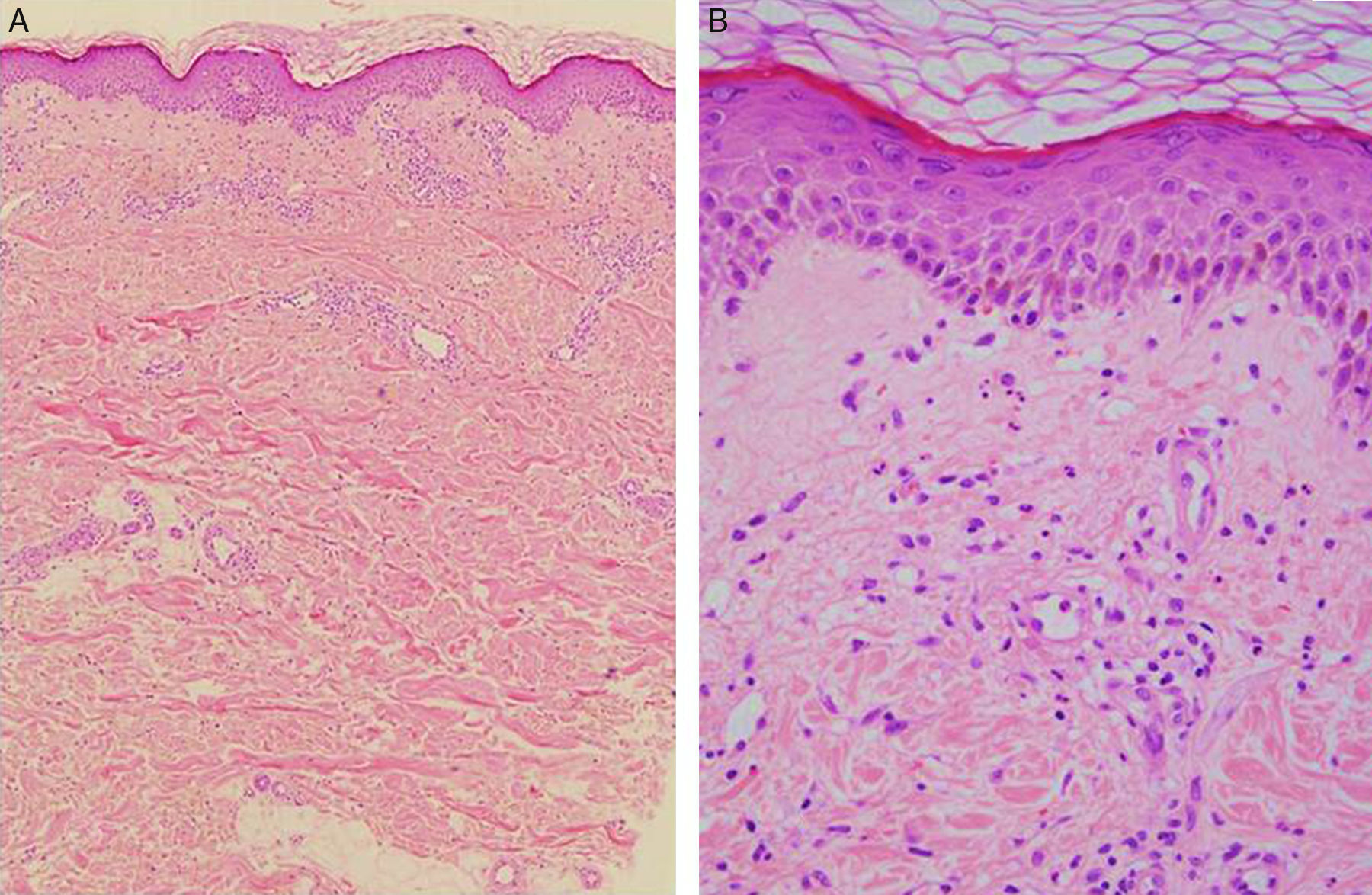
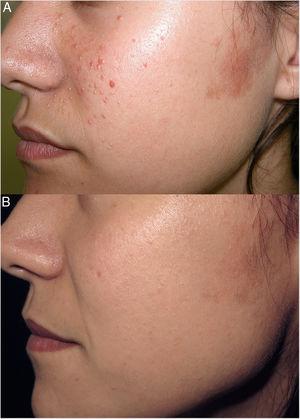
A 66-year-old woman had been diagnosed with RA 22 years earlier. She met 5 of the criteria established for RA2: morning stiffness, arthritis of hand joints, symmetric arthritis, positive serum rheumatoid factor, and compatible radiographic changes. Since then, she had been taking metamizole and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and had achieved good control. Eight years after the diagnosis, she experienced a severe flare-up and developed bilateral rheumatoid nodules on her elbows. Leflunomide (300mg/d for 5 days and maintenance with 20mg/d) was added and no adverse effects were noted. She unilaterally decided to stop taking leflunomide 4 years ago because she considered that her disease was well controlled. Since then, she has only taken metamizole occasionally. She underwent a total left knee arthroplasty 2 years before being referred to our dermatology department in January 2011 with a painful lesion that had appeared a month earlier. The patient explained that the lesion had begun around the ankle and spread toward her left knee. Physical examination revealed a large plaque with polycyclic erythematous-edematous borders around the superior aspect of the knee (Fig. 1A). Lymphedema was present as a complication of the knee arthroplasty. There were no reports of infection or medication use in the preceding month. There was also no fever, malaise, myalgia, or lymphadenopathy. The following blood tests showed normal findings: hemogram, biochemistry, C protein reactive, and screening for auto-antibodies. The chest and knee X-rays were also unremarkable. Microscopic examination of a skin biopsy revealed discrete spongiosis in the epidermis and a moderate superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and numerous neutrophils in the dermis (Fig. 2A and B). There was no edema or evidence of vasculitis. Oral prednisone 40mg/d resolved this episode and was progressively withdrawn. In March 2012, the inflammatory margins progressed centrifugally to the medial aspect of the thigh (Fig. 1B). Another skin biopsy was performed and showed the same results. In order to rule out underlying malignancy, a cranial–cervical–thoracic–abdominopelvic computed tomography scan and mammography were performed, with unremarkable results. Serum tumor markers were all normal.
In September 2012 the patient experienced another outbreak, which extended up as far as the gluteus and left hip and thoracic side (Fig. 1C). Treatment with dapsone 50mg/d was commenced. In February 2013, annular plaques appeared on both shoulders and the proximal aspects of her arms. Colchicine was added and the symptoms resolved within a few days. Currently, the patient is receiving dapsone 100mg/d plus colchicine and has experienced no further episodes.
We have presented a case in which a patient with RA developed a painful form of CRAND with a unique wave-like clinical course. Our patient had 2 of the main predisposing factors for neutrophilic illness: lymphedema and RA. Lymphedema, which can lead to the accumulation of protein-rich interstitial fluid containing high levels of cytokines and chemokines that might attract neutrophils,3,4 has been reported as a risk factor for Sweet syndrome.3 RA, in turn, has been associated with a wide range of neutrophilic dermatoses.5 However, to our knowledge, this is the first report concerning RA-associated CRAND.
CRAND is very rare and only 4 cases have been reported to date. Its etiology is unknown and no association has been detected with drugs, infections, or systemic illness. Clinically, it is characterized by recurrent outbreaks of generalized painful annular plaques with erythematous-edematous borders and a lilaceous center.6,7 Fever, general symptoms, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia are absent. The present case is unique because of its clinical course. Inflammatory margins advanced upwards only, from the ankle to the arms, in a striking wave-like pattern, and there have been no recurrences in 2 years of follow up. Histopathological examination shows a neutrophilic infiltration in the mid and upper dermis, with no signs of vasculitis.1 Corticosteroids are useful for resolving occasional events.6 Treatment with potassium iodide has also been attempted.7 The neutrophilic infiltration in our patient led us to use dapsone, which inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis. The combination of dapsone 150mg/d and colchicine has been successful and there have been no further recurrences.
In conclusion, we have reported a rare and interesting case of CRAND that had several unique aspects: a striking wave-like clinical course, a novel association with RA, and successful treatment with dapsone plus colchicine to prevent additional outbreaks. Although CRAND may be considered a controversial entity due to its rarity, we consider that this descriptive term is the most suitable to describe the present case since our patient did not fulfill the criteria for any other condition and experienced chronic, relapsing annular neutrophilic lesions.