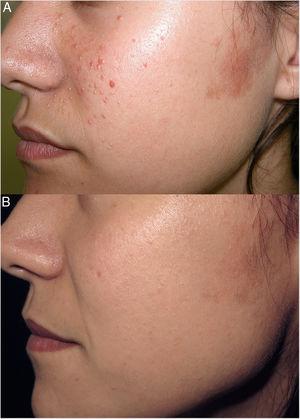
In recent years, a series of new drugs have been developed through the application of molecular biology. These drugs act by blocking specific molecules of the immune system and have been developed to act on specific targets that play an important role in the pathophysiology of the diseases in which their therapeutic use has now been approved. Over time, experience has been accumulated in the use of these drugs in the treatment of skin diseases for which they have not been approved but in which the pathophysiology suggests that they could also be effective. The use of these drugs is increasing in difficult-to-treat cases of skin diseases for which the drugs are not approved. The second part of this review of off-label use of biologic agents in dermatology considers the use of etanercept, efalizumab, alefacept, rituximab, basiliximab, omalizumab, and cetuximab.
En los últimos años han aparecido una serie de nuevos fármacos desarrollados por biología molecular. Estos medicamentos actúan bloqueando moléculas específicas del sistema inmunológico y se desarrollan para actuar sobre dianas específicas que tienen un papel importante en la fisiopatología de determinadas enfermedades para cuyo tratamiento son aprobadas. Con el tiempo se ha ido adquiriendo experiencia con estos medicamentos en el tratamiento de dermatosis para las que no han sido diseñados, pero para las que, por compartir un mismo mecanismo fisiopatológico, pueden ser útiles. El empleo de estos medicamentos en el tratamiento de casos difíciles de numerosas enfermedades dermatológicas para las cuales no están aprobados es creciente. Esta segunda parte de la revisión analiza el uso, fuera de indicación, en el tratamiento de la dermatosis de los siguientes fármacos biológicos: etanercept, efalizumab, alefacept, rituximab, daclizumab, basiliximab, omalizumab y cetuximab.