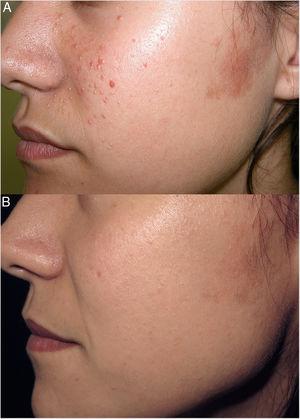
We read with interest the case and research letter by Marcoval et al.1 regarding 2 cases of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. We were surprised that the letter did not mention Laugier disease (or Laugier-Hunziker syndrome), an entity characterized by essential cutaneous and mucosal pigmentation, originally described on the lips and oral mucosa and, at times, associated with longitudinal melanonychia.2
In 1998, we reported 9 cases of Laugier disease, in 1 man and 8 women.3 Two of the women presented punctate pigmentation of the tongue identical to the cases reported by Marcoval et al.1 One of these patients also had hyperpigmented lesions affecting the oral mucosa, gums, labia menora, and nails. The other presented pigmentation of the lips, gums, oral mucosa, and lateral nail folds on some fingers.
We have found reports of other similar cases described as Laugier-Hunziker syndrome; these patients presented punctate pigmentation of the lingual papillae as described by Marcoval et al.1 in association with pigmentation of the nails,4 the lower lip and the toes and fingers,5 and in one case the oral mucosa, the lips, and the nails.6 We believe that all of these case reports, including that of Marcoval et al.,1 correspond to the same process—hyperpigmentation of unknown etiology affecting the lips, oral mucosa, tongue (fungiform papillae), nails, genitals, and perhaps other areas in a variety of ways, in combination or alone.
After we reported our series as Laugier disease, we were criticized for omitting Hunziker from the eponymous name.7 Our use of the term Laugier disease followed the example of French authors, who preferred this name to that of idiopathic pigmentation of the mucosa, a term that does not include the involvement of the nails. Another reason for our choice was that, in several published reports, the process was considered to be Laugier-Hunziker syndrome only when pigmentation of the oral mucosa was associated with longitudinal melanonychia, a distinction that gave rise to some confusion.
In response to the criticism, we put forward our view of what the process should be called when new reports appeared of combined involvement of the oral mucosa and the nails, and in the case of similar lesions affecting the genitals, conjunctiva, larynx, or esophagus as well as other combinations of pigmentation and even isolated lesions affecting only the nails or only a mucosal membrane.8 Shortly thereafter, in line with our reasoning concerning variations of the earlier descriptions, a report was published of a case involving the oral mucosa, lip, palate, palm, and esophagus in which the authors referred to the process as Laugier-Hunziker syndrome associated with esophageal melanocytosis.9 This was the first description of such a combination. Histologic study of biopsy specimens showed acanthosis and basal pigmentation in the esophagus, on the lip and on the palms. Three years earlier, a case had been reported of a patient with pigmented lesions on the lips and oral mucosa associated with pigmentation of several fingers, the eyebrows, and the heels. The title of that article described the case as Laugier-Hunziker syndrome with atypical features and the authors reported that they had considered the possibility of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, albeit incomplete because of the absence of intestinal polyposis.10
In summary, several different idiopathic pigmentation disorders of the skin, nails, oral mucosa, and genitals exist, and a variety of names have been used to denominate them. Because of the large number of names used, all probably referring to the same entity, we approve of the proposal by Seoane et al.11 that this condition be called essential mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation. However, as this term encompasses the idea of concurrent involvement of the skin and mucous membranes, which—as we have shown—is extremely variable, we consider that the designation should be essential cutaneous and/or mucosal hyperpigmentation or even essential melanin pigmentation of the skin, mucous membranes, or nails. This last designation reflects the melanocytic origin of the condition and the variable involvement in a more detailed and well-defined way; it could also be rendered simply as essential melanin pigmentation (of Laugier-Hunziker if you will), a name that would do justice to the initial description.
The condition is not as rare as it was thought and we believe that its incidence is influenced by a certain racial predisposition in which some unknown factor triggers the appearance of lesions by way of an increase in the synthesis of melanosomes, with idiosyncratic involvement of a variety of sites which, for unknown reasons, are more susceptible to this condition and vary from case to case.
The principal histologic features are hyperpigmentation of the basal layer without increased melanocytes, associated with acanthosis and the presence of melanophages, and a variable chronic inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis.
As this is not a disease or a syndrome, to facilitate naming the entity, some form of eponym will probably come to predominate over the long term.
Please cite this article as: Urbina F, Sudy E. Pigmentación de las papilas fungiformes linguales en la enfermedad de Laugier (o síndrome de Laugier-Hunziker). Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013;104:173-4.